Disease Overview:
Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) is a multifaceted skin condition marked by the unexpected development of hives, angioedema, or both, persisting for over six weeks. In numerous cases, individuals endure a fluctuating pattern of symptoms that can recur over several years.
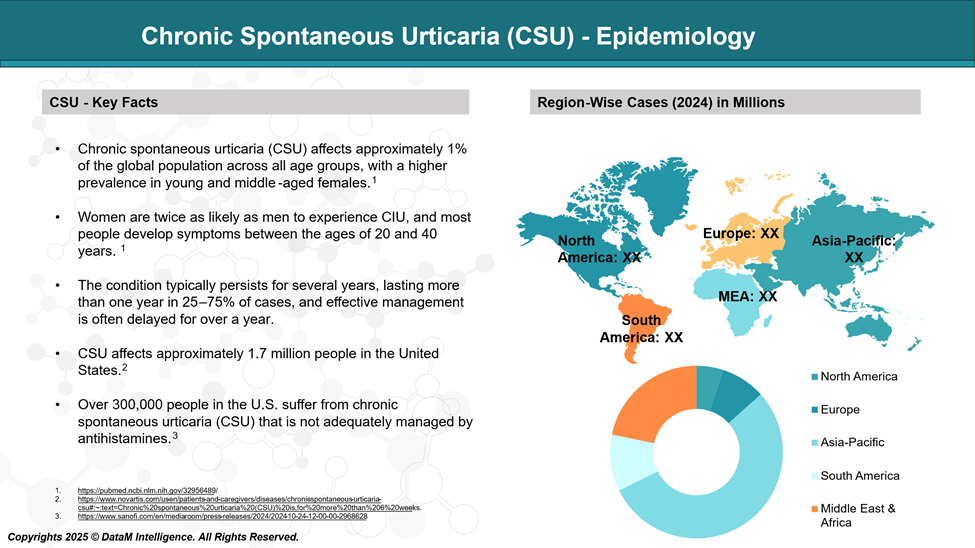
Epidemiology Analysis (Current & Forecast)
CSU most commonly occurs between the ages of 20 and 40, typically lasting one to five years, though it may persist longer in more severe cases. It affects approximately 1% of the general population, with women being twice as likely to be affected as men.
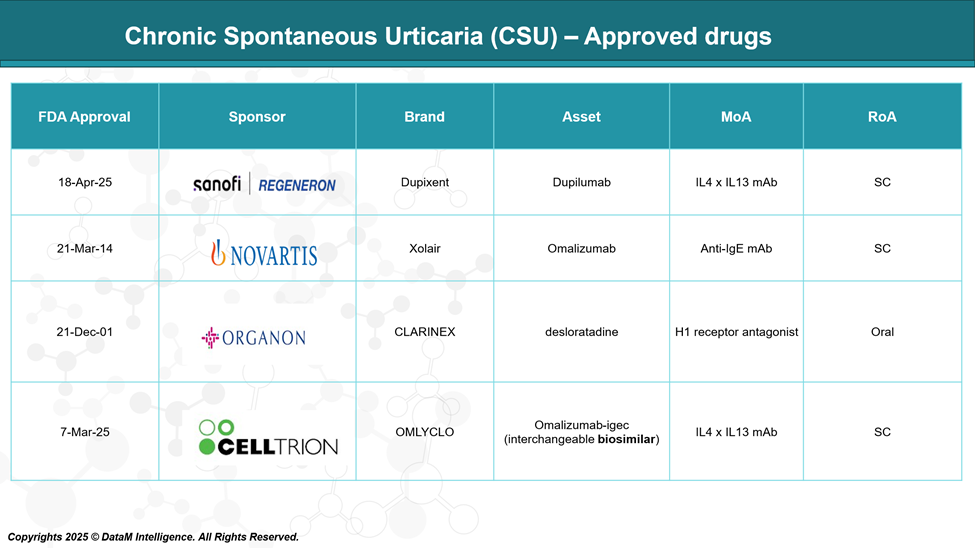
Approved Drugs - Sales & Forecast
Several medications have been approved for the treatment of chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU), targeting different pathways involved in the disease's pathogenesis. These include antihistamines, monoclonal antibodies, and biologic agents aimed at reducing inflammation and suppressing immune overactivation.
The availability of both original biologics and biosimilars has expanded therapeutic options, improving symptom control and patient outcomes.
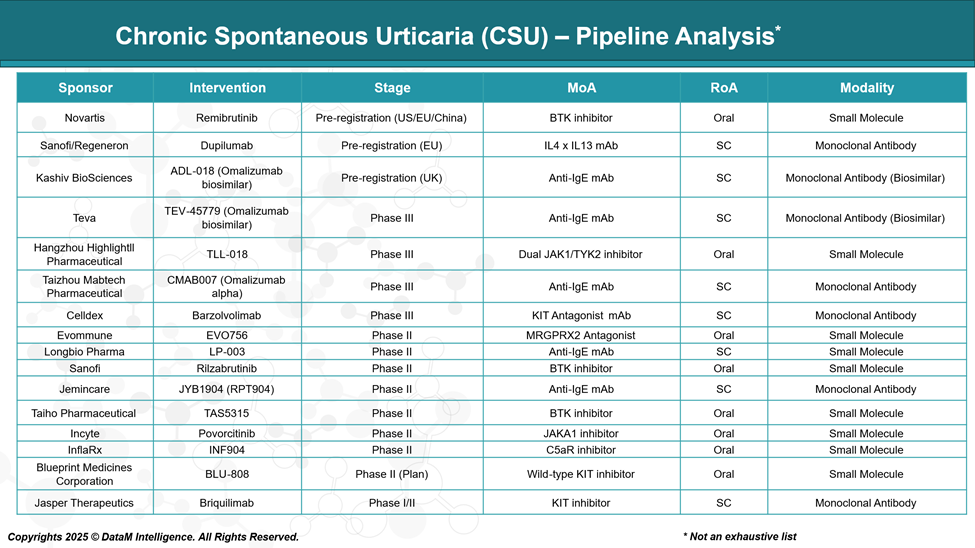
Pipeline Analysis and Expected Approval Timelines
The therapeutic landscape for chronic spontaneous urticaria is evolving rapidly, with numerous investigational agents in development aimed at addressing unmet clinical needs, particularly for patients who remain symptomatic despite current therapies.
The CSU pipeline includes a range of novel biologics, small molecules, and biosimilars targeting key pathways such as IgE, IL-4/IL-13, the BTK inhibitors, KIT inhibitors, and the complement system.
Competitive Landscape and Market Positioning
The competitive landscape for prurigo nodularis (PN) is undergoing a dynamic shift as more pharmaceutical companies enter the field with novel therapies targeting key immunological pathways. The market, once underserved, is now becoming a high-interest area driven by the approvals of Dupixent (dupilumab) and Nemluvio (nemolizumab) and a robust pipeline of late-stage candidates.
Company | Product | MoA | Development Stage | Differentiation / Key Advantage | Market Positioning |
Sanofi / Regeneron | Dupixent (dupilumab) | IL-4/IL-13 mAb | Approved / Pre-reg (EU) | Targets type 2 inflammation; effective in multiple atopic diseases | Positioned for biologic-refractory CSU; premium biologic |
Novartis | Xolair (omalizumab) | Anti-IgE mAb | Approved | First and leading biologic for CSU; strong real-world data | Gold standard: strong physician trust |
Organon | CLARINEX (desloratadine) | Antihistamine (H1 antagonist) | Approved | Oral, affordable first-line therapy | Entry-level, symptom control |
Celltrion | OMLYCLO (omalizumab-igec) | Omalizumab biosimilar | Approved | Interchangeable biosimilar; cost advantage | Market disruptor for anti-IgE class |
Novartis | Remibrutinib | BTK inhibitor | Pre-registration (US/EU/China) | Oral small molecule; novel MoA for CSU | Potential Xolair alternative for antihistamine-refractory cases |
Sanofi / Regeneron | Dupilumab | IL-4/IL-13 mAb | Pre-registration (EU) | Expanding regulatory footprint in CSU | Growth driver in EU market |
Kashiv BioSciences | ADL-018 | Omalizumab biosimilar | Pre-registration (UK) | Biosimilar cost benefit | Competitive biosimilar play |
Teva | TEV-45779 | Omalizumab biosimilar | Phase III | Anti-IgE biosimilar; expands biosimilar pipeline | Increases anti-IgE class competition |
Taizhou Mabtech | CMAB007 (Omalizumab alpha) | Anti-IgE mAb | Phase III | Novel anti-IgE with potential for improved binding | Positioned as next-gen omalizumab |
Hangzhou Highlightll | TLL-018 | Dual JAK1/TYK2 inhibitor | Phase III | Oral; new MoA for CSU | Non-biologic alternative; novel pathway |
Celldex | Barzolvolimab | KIT antagonist mAb | Phase III | Mast cell-targeting biologic; unique approach | High potential in severe or biologic-refractory CSU |
Key Takeaways
- Xolair leads the market but faces growing biosimilar pressure.
- Dupilumab and remibrutinib are strong contenders offering differentiated mechanisms.
- Biosimilars like OMLYCLO, ADL-018, and TEV-45779 are set to disrupt pricing and access.
- Novel entrants (Barzolvolimab, TLL-018) provide unique mechanisms aimed at unmet needs in refractory cases.
Key Companies:

Target Opportunity Profile (TOP)
Here's a Target Opportunity Profile outlining the ideal attributes that emerging therapies for chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU), should demonstrate to surpass currently approved treatments like Xolair (omalizumab) and Dupixent (dupilumab):
Target Opportunity Profile for Emerging CSU Drugs
Attribute | Optimal Target Profile | Rationale / Competitive Advantage |
Efficacy | - Rapid onset of action (≤ 2 weeks) | Faster and more complete symptom relief vs. existing biologics; addresses patient dissatisfaction |
Safety / Tolerability | - Clean safety profile with minimal systemic immunosuppression | To improve on safety concerns seen with omalizumab (e.g., anaphylaxis risk) and broader biologic use |
Mechanism of Action (MoA) | - Novel and disease-specific pathway (e.g., BTK, KIT, JAK1/TYK2, mast cell inhibition) | Differentiation from anti-IgE/IL-4/IL-13; addresses non-type 2 and refractory CSU subsets |
Route of Administration (RoA) | - Oral or less frequent subcutaneous (e.g., monthly SC or longer) | Oral or infrequent injection improves adherence and patient convenience |
Dosing / Convenience | - Low, infrequent dosing (e.g., once monthly or oral daily) | Matches or exceeds Xolair’s and Dupixent’s dosing schedules |
Innovation / Differentiation | - First-in-class or best-in-class | Fills unmet need in refractory cases; sets new treatment standard |
Onset & Duration | - Onset within 1–7 days | Early response reduces corticosteroid use; durable effect improves quality of life |
Patient Subgroup Targeting | - Effective in anti-IgE and anti-IL-4/13 non-responders | Broadens market capture; addresses difficult-to-treat populations |
Biomarker Support / Precision | - Companion diagnostics or predictive biomarkers to stratify responders | Supports personalized treatment; payer and clinician adoption driver |
Regulatory / Access Strategy | - Global filings (US/EU/Asia) | Ensures broad reach and competitive positioning against branded and biosimilar rivals |
Summary Insight
To compete with established agents like Xolair and Dupixent, emerging CSU therapies must offer faster, more durable efficacy, a safer or more convenient profile, and target novel pathways to benefit patients who fail current biologics. Additionally, oral agents, innovative MoAs, and biomarker-driven personalization will play a critical role in differentiating and positioning these therapies competitively.
Why Buy Our Pharma Competitive Intelligence Report?
Our Pharma Competitive Intelligence Report is designed to give you a strategic advantage by providing deep insights into the pharmaceutical landscape. Here’s how it benefits you and your business: