Disease Overview:
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) ranks among the most prevalent and severe inherited kidney disorders. It is characterized by the progressive formation of numerous fluid-filled cysts in both kidneys, which can enlarge over time and impair kidney function. Eventually, this condition often results in kidney failure, making it the fourth most common cause of end-stage renal disease.
Epidemiology Analysis (Current & Forecast)
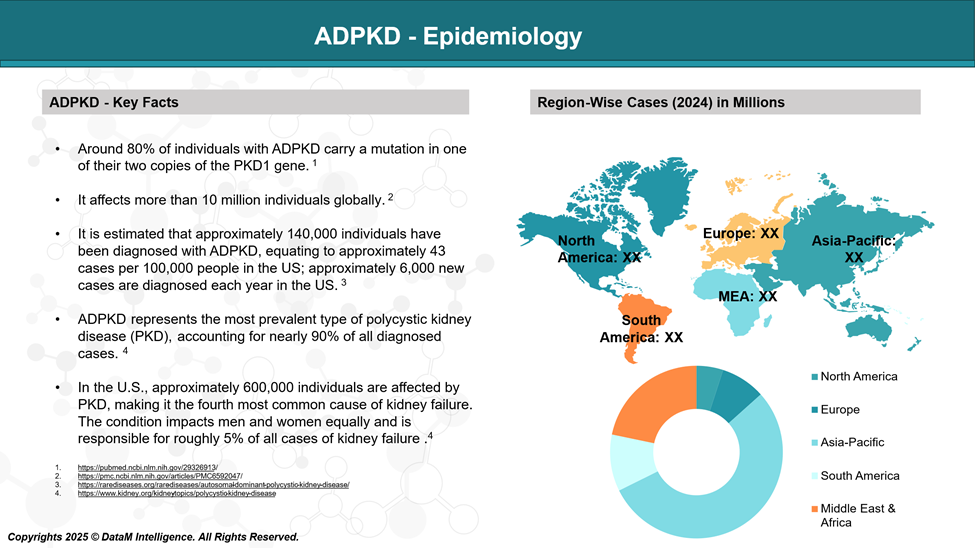
ADPKD occurs in approximately 1 in every 1,000 individuals and is responsible for around 5% of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) cases that require renal replacement therapy. Although symptoms typically do not appear until adulthood, the condition has nearly full penetrance, meaning that by age 80, almost all affected individuals will show some clinical signs of the disease.
Approved Drugs - Sales & Forecast
As of now, the only FDA-approved drug specifically for treating ADPKD is:
Tolvaptan (brand name: Jynarque) - Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd
Mechanism: Tolvaptan is a selective vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist. It works by reducing cyst growth and slowing the decline of kidney function.
Indication: Approved for use in adults at risk of rapidly progressing ADPKD.
Approval: FDA approved in April 2018.
Usage: Taken orally, typically in a split-dose regimen (a higher dose in the morning and a lower dose in the afternoon).
Side Effects: Includes increased urination, thirst, liver enzyme elevations, and potential liver injury patients on tolvaptan require regular liver function monitoring.
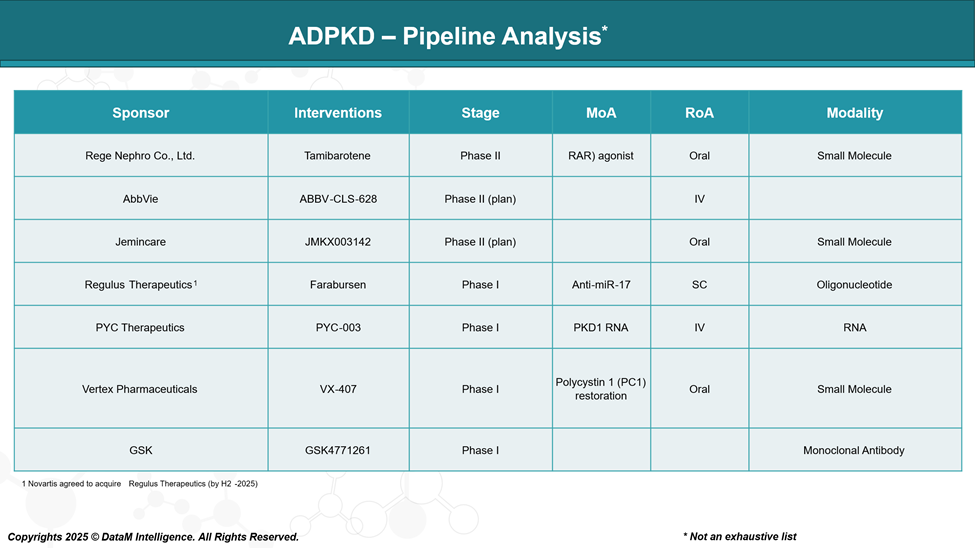
Pipeline Analysis and Expected Approval Timelines
The treatment landscape for ADPKD is expanding beyond the currently approved therapy, tolvaptan. Several promising drug candidates are in various stages of clinical development, aiming to address the underlying mechanisms of the disease and improve patient outcomes.
Competitive Landscape and Market Positioning
Tolvaptan remains the only FDA- and EMA-approved therapy for slowing kidney function decline in ADPKD. As the sole market entrant, it enjoys first-mover advantage, established clinical utility, and brand recognition.
Strengths:
Proven efficacy in delaying disease progression (e.g., TEMPO 3:4 and REPRISE trials).
Strong physician familiarity and payer adoption.
Oral dosing suits outpatient management.
Limitations:
Hepatotoxicity risk requiring regular liver monitoring.
Patient adherence challenges due to aquaretic side effects (polyuria, thirst).
These limitations create a significant opportunity for differentiated therapies.
Emerging Therapies:
A wave of next-generation therapies is advancing through early-stage clinical development, offering diverse mechanisms of action and targeting various unmet needs.
Sponsor | Drug Candidate | Stage | Unique Positioning | Target Patient Benefit | Strategic Outlook |
Rege Nephro Co., Ltd. | Tamibarotene | Phase II | Oral alternative with anti-inflammatory potential | Improved tolerability and fibrosis management | May serve as a more tolerable option to Tolvaptan |
AbbVie | ABBV-CLS-628 | Phase II (planned) | Undisclosed, likely novel biologic | Potential for long-acting or first-in-class effect | High-profile sponsor with capacity for rapid scale |
Jemincare | JMKX003142 | Phase II (planned) | Oral small molecule under-the-radar | Cost-effective oral therapy | May compete on pricing and regional access |
Regulus Therapeutics | Farabursen | Phase I | First-in-class microRNA-targeted therapy | Disease modification at gene expression level | Unique scientific angle, potential for fast-track |
PYC Therapeutics | PYC-003 | Phase I | Targets PKD1 RNA to correct the root mutation | Precision therapy for genetically confirmed cases | Differentiated but early-stage and complex delivery |
Vertex Pharmaceuticals | VX-407 | Phase I | Targets the restoration of polycystin-1 protein | Addresses the root genetic cause of ADPKD | High innovation potential, long development path |
GSK | GSK4771261 | Phase I | Undisclosed, large-molecule potential | Long-acting therapy, reduced dosing burden | Big Pharma muscle, unknown differentiation yet |
Strategic Insights Summary
- Vertex and Regulus offer genetic or transcriptomic precision, a key differentiator in long-term disease modification.
- Rege Nephro and Jemincare may be fast followers aiming for better-tolerated or cheaper oral alternatives.
- AbbVie and GSK bring biologics and systemic therapy potential with stronger resource backing.
- While Tolvaptan retains a commanding position, the pipeline reflects a competitive and innovation-rich environment. Among emerging therapies:
Who Has the Edge?
Vertex’s VX-407 and Regulus’s Farabursen are scientifically differentiated and potentially disruptive.
Tamibarotene offers a near-term opportunity for oral, better-tolerated therapy.
GSK and AbbVie may leverage biologics expertise for long-acting or synergistic treatments.
Key Companies:

Target Opportunity Profile (TOP)
The Target Opportunity Profile (TOP) outlines the critical attributes new ADPKD treatments must exhibit to gain a competitive advantage and better meet patient and healthcare system needs.
Attribute | Current Standard (Tolvaptan) | Opportunity for Emerging Therapies |
Safety | Risk of hepatotoxicity requiring frequent liver monitoring; aquaretic side effects (polyuria, thirst) impacting quality of life | Significantly improved safety profile with minimal liver toxicity; fewer or milder side effects to improve patient adherence and QOL |
Efficacy | Proven to slow cyst growth and decline in kidney function, but not a cure; effectiveness varies among patients | Equal or superior efficacy in slowing or halting disease progression; potential for disease modification or reversal by targeting root causes |
Mechanism of Action (MoA) | Vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist reduces cAMP signaling to slow cyst growth | Novel or complementary MoA, such as genetic correction (PC1 restoration), microRNA modulation, anti-inflammatory, or fibrosis-targeting approaches |
Route of Administration (RoA) | Oral, twice daily dosing with fluid intake restrictions | Oral preferred but with flexible dosing regimens (once daily or less frequent); potential for subcutaneous or intravenous delivery if justified by improved efficacy or safety |
Dosage Convenience | Twice daily dosing, which can impact compliance | Simplified dosing schedule (once daily or less frequent) to enhance adherence; extended-release formulations or long-acting injectables could be advantageous |
Modality | Small molecule | Innovation in modality—such as RNA-based therapies, oligonucleotides, monoclonal antibodies, or gene therapies—that provide targeted, durable effects with manageable administration |
Innovation | First-in-class with well-characterized target | Significant innovation beyond vasopressin antagonism, potentially addressing underlying genetic mutations or disease pathways for more sustained benefit |
Patient Population | Approved mainly for adults at risk of rapidly progressing ADPKD | Broader applicability across disease stages, including early intervention or those intolerant to tolvaptan |
Monitoring Requirements | Frequent liver function tests and monitoring for side effects | Reduced monitoring burden, making therapy easier to manage in routine clinical practice |
Cost and Access | High cost and variable reimbursement | Competitive pricing and better access strategies, potentially improving uptake and adherence |
What Emerging Drugs Must Deliver
To successfully compete and potentially replace or complement tolvaptan, new ADPKD therapies should:
- Demonstrate a better safety and tolerability profile, especially avoiding liver toxicity.
- Show equal or superior efficacy, ideally through novel mechanisms addressing the disease at its genetic or molecular roots.
- Provide patient-friendly administration, favoring less frequent dosing and convenient routes.
- Incorporate innovative modalities that offer durable disease modification.
- Reduce the need for intensive monitoring, thereby lowering treatment burden.
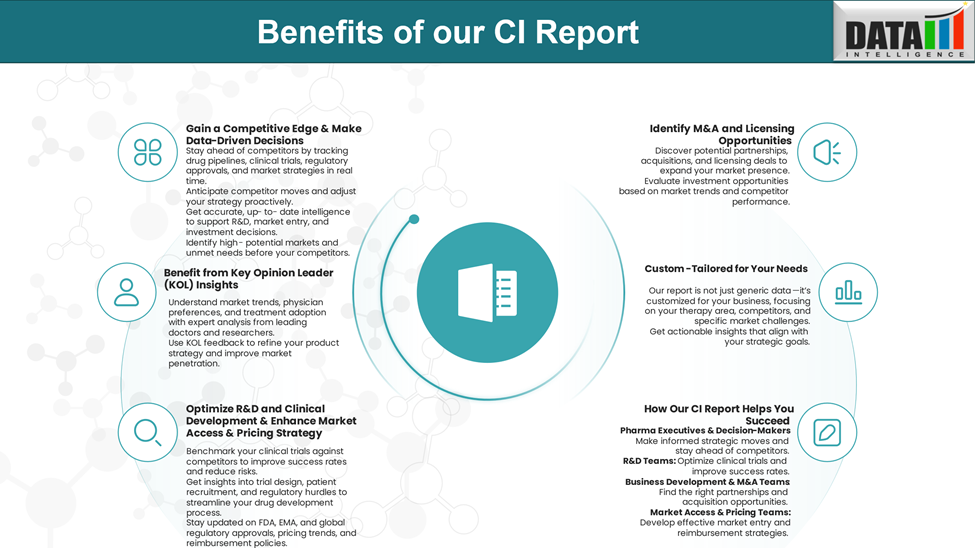
Why Buy Our Pharma Competitive Intelligence Report?
Our Pharma Competitive Intelligence Report is designed to give you a strategic advantage by providing deep insights into the pharmaceutical landscape. Here’s how it benefits you and your business: