Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillators Market Size
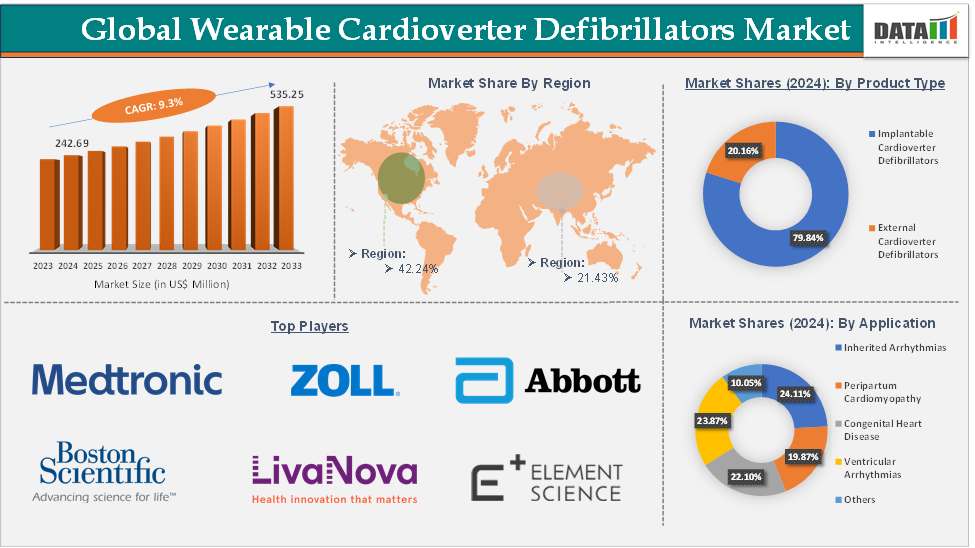
Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillators Market size reached US$ 242.69 Million in 2024 and is expected to reach US$ 535.25 Million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 9.3% during the forecast period 2025-2033.
Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillators Market Overview
The global wearable cardioverter defibrillators market is experiencing significant growth, driven by advancements in cardiac care technology and the increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases. The market is also poised for substantial growth, driven by technological innovations, an aging population, and the integration of telehealth solutions. However, addressing challenges such as high costs, regulatory hurdles, and awareness gaps will be crucial for maximizing market potential. Stakeholders must focus on enhancing accessibility and education to ensure the widespread adoption of WCDs in managing sudden cardiac arrest risks.
Executive Summary
For more details on this report – Request for Sample
Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillators Market Dynamics: Drivers & Restraints
The rising incidence of sudden cardiac arrest is significantly driving the wearable cardioverter defibrillators market growth
According to the National Institute of Health, around 2 million sudden cardiac death (SCD) cases are reported each year worldwide. This high incidence and the associated mortality and morbidity make sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) and SCD major global public health problems. As the incidence of sudden cardiac arrest continues to rise due to various factors like an aging population, higher cardiovascular disease rates, and increasing SCA cases, the wearable defibrillator market is expected to grow significantly. Wearable cardioverter defibrillators offer a practical, life-saving solution for high-risk individuals, fueling both demand and market expansion.
As awareness grows around conditions that lead to SCA, such as arrhythmias, congenital heart defects, or a history of heart disease, more patients and healthcare providers are recognizing the importance of wearable defibrillators as an essential preventive measure. The rise in cardiovascular diseases, especially in older populations, is leading to higher rates of SCA. For instance, athletes and individuals with hereditary conditions like Long QT Syndrome are more prone to sudden cardiac events, thus accelerating demand for wearable defibrillators.
Limited battery life and device downtime are hampering the wearable cardioverter defibrillators market growth
Wearable cardioverter defibrillators, such as ZOLL's LifeVest, require regular charging or battery replacement, typically every 24-48 hours. This frequent downtime can be inconvenient for patients, especially for those in critical conditions or living in remote areas where access to charging facilities is limited. The need for frequent recharging undermines the reliability of the device, as patients may forget or fail to recharge it in time, thus leaving them unprotected during critical moments.
As the battery reaches the end of its lifespan, it can lead to potential malfunctions or the failure of the device to deliver appropriate shocks. In high-risk cardiac patients, such failures can result in severe consequences, including death. These technical limitations reduce the perceived reliability of wearable cardioverter defibrillators, making healthcare providers and patients wary of using them over long periods.
Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillators Market Segment Analysis
The global wearable cardioverter defibrillators market is segmented based on product type, application, end-user, and region.
Product Type:
The implantable cardioverter defibrillators from the product type segment are expected to hold 79.84% of the market share in 2024 in the wearable cardioverter defibrillators market
Implantable cardioverter defibrillators offer continuous, uninterrupted protection against sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) and arrhythmias, unlike external wearable defibrillators (WCDs), which are intended as temporary solutions. Implantable cardioverter defibrillators are implanted directly into the patient’s chest and monitor heart rhythms around the clock, automatically delivering shocks when necessary. This permanent protection eliminates the need for recharging or device downtime, which is a challenge for WCDs.
Implantable cardioverter defibrillators have evolved with advanced features like leadless systems, automatic arrhythmia detection, and remote monitoring. These features make implantable cardioverter defibrillators more sophisticated, adaptable, and integrated into modern healthcare systems. In contrast, wearable defibrillators (WCDs) are limited in functionality, primarily serving as a bridge before permanent implantation.
For instance, in March 2025, Medtronic launched its Aurora EV-ICD system for treating ventricular arrhythmias in Japan. They comprise the implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) system that performs electrotherapy to restore the heart to a normal rhythm. Aurora delivers defibrillation, anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP) and backup (pause-prevention) pacing therapies. It features a similar size, shape and longevity to traditional transvenous ICDs. This technology improves patient outcomes, making ICDs more desirable in managing high-risk patients.
Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillators Market Geographical Analysis
North America is expected to dominate the global wearable cardioverter defibrillators market with a 42.24% share in 2024
The high incidence of cardiovascular diseases in North America, particularly in the U.S., drives the demand for cardiac monitoring devices like wearable cardioverter defibrillators. According to the American Heart Association, heart disease remains the leading cause of death in the U.S., and conditions like arrhythmias and sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) are becoming more common due to an aging population, sedentary lifestyles, and increased rates of obesity and diabetes.
North America benefits from comprehensive insurance reimbursement systems, particularly in the U.S., which make wearable cardioverter defibrillators more accessible to patients. The widespread Medicare and private insurance coverage of wearable defibrillators has contributed significantly to their adoption, making them a viable option for patients who otherwise might not be able to afford the device.
For instance, in January 2024, Kestra Medical Technologies announced that the ASSURE Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillator (WCD) system is available to cover over 200+ million health plan members across the U.S. The company reached this covered-lives milestone less than eighteen months after commencing the national commercial launch phase of the ASSURE system in the U.S. The more than 200 million total covered lives include broad coverage for members of all national commercial insurers and many of the regional commercial insurers and networks, including Cigna, Premera, CareCentrix, Florida Blue, and multiple other Blue Cross Blue Shield (BCBS) plans.
Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillators Market Top Companies
Top companies in the wearable cardioverter defibrillators market include Medtronic, ZOLL Medical Corporation, Abbott, Boston Scientific Corporation, LivaNova PLC, Koninklijke Philips N.V., Element Science, and Kestra Medical Technologies, Inc., among others.
Market Scope
| Metrics | Details | |
| CAGR | 9.3% | |
| Market Size Available for Years | 2022-2033 | |
| Estimation Forecast Period | 2025-2033 | |
| Revenue Units | Value (US$ Mn) | |
| Segments Covered | Product Type | Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators and External Cardioverter Defibrillators |
| Application | Inherited Arrhythmias, Peripartum Cardiomyopathy, Congenital Heart Disease, Ventricular Arrhythmias, and Others | |
| End-User | Hospitals, Cardiac Clinics, Homecare Settings, and Others | |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and the Middle East & Africa | |
The global wearable cardioverter defibrillators market report delivers a detailed analysis with 56 key tables, more than 52 visually impactful figures, and 157 pages of expert insights, providing a complete view of the market landscape.

