Overview of Stem Cell Therapy
Hook
Stem cell therapy has emerged as a beacon of hope in modern medicine. Over 116 clinical trials are currently underway, exploring its potential to treat conditions ranging from neurodegenerative diseases to various forms of cancer. This rapidly evolving field is not only reshaping the landscape of medical treatments but also igniting discussions about the future of healthcare. The significant number of clinical trials indicates a robust investment in research and development, underscoring the urgency and promise of stem cell applications.
Definition
Stem cell therapy involves using stem cells to prevent or treat diseases and injuries. These unique cells can develop into different cell types, making them invaluable for regenerative medicine. Their significance lies in their potential to heal damaged tissues, restore function, and even cure previously untreatable conditions. By harnessing the power of stem cells, researchers and clinicians are paving the way for innovative therapies that could transform patient care. This adaptability allows stem cells to be utilized in a wide range of medical applications, from repairing heart tissue after a heart attack to regenerating nerve cells in spinal cord injuries.
What Are Stem Cells?
- Stem cells are exceptional cells distinguished by their unique ability to self-renew and differentiate into various specialized cell types. They possess two fundamental properties that differentiate them from other cell types.
- The adaptability of stem cells is crucial for their application in therapies targeting a wide range of medical conditions, including degenerative diseases, injuries, and genetic disorders.
Properties of Stem Cells
| Self-Renewal | Differentiation |
Stem cells can undergo multiple cycles of cell division while preserving their undifferentiated state. This characteristic enables them to maintain and replenish their population over time. | Stem cells have the extraordinary capability to differentiate into specialized cells that perform specific functions within the body, such as muscle cells, nerve cells, or blood cells. |
Types of Stem Cells
- Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs)
- Adult Stem Cells (Somatic Stem Cells)
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
- Totipotent Stem Cells
Types of Stem Cell Therapies
- Autologous Stem Cell Therapy
- Allogeneic Stem Cell Therapy
- Cord Blood Stem Cell Therapy
- Stem Cell Transplantation
- Gene Therapy Combined with Stem Cell Therapy
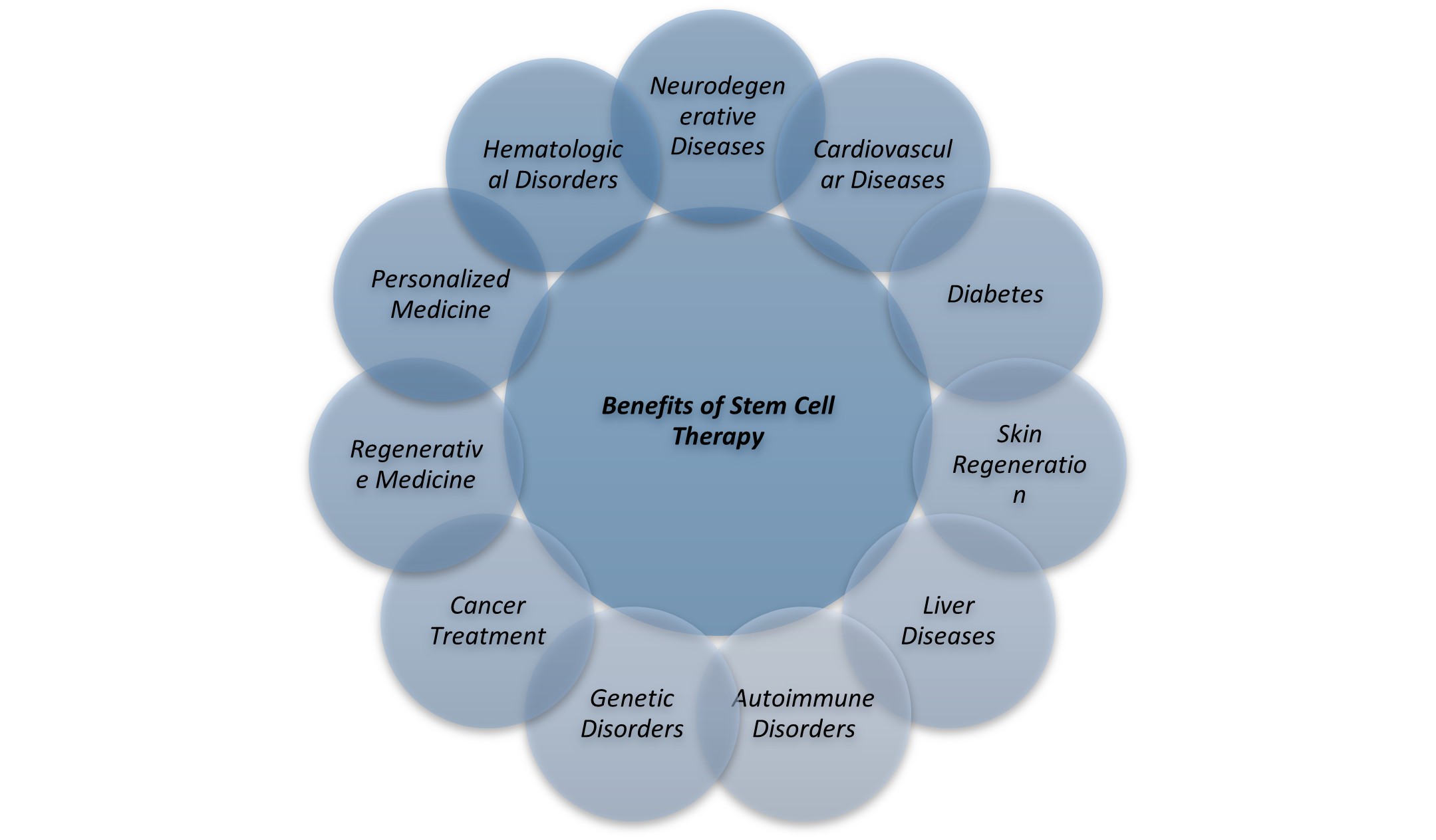
Applications of Stem Cell Therapy
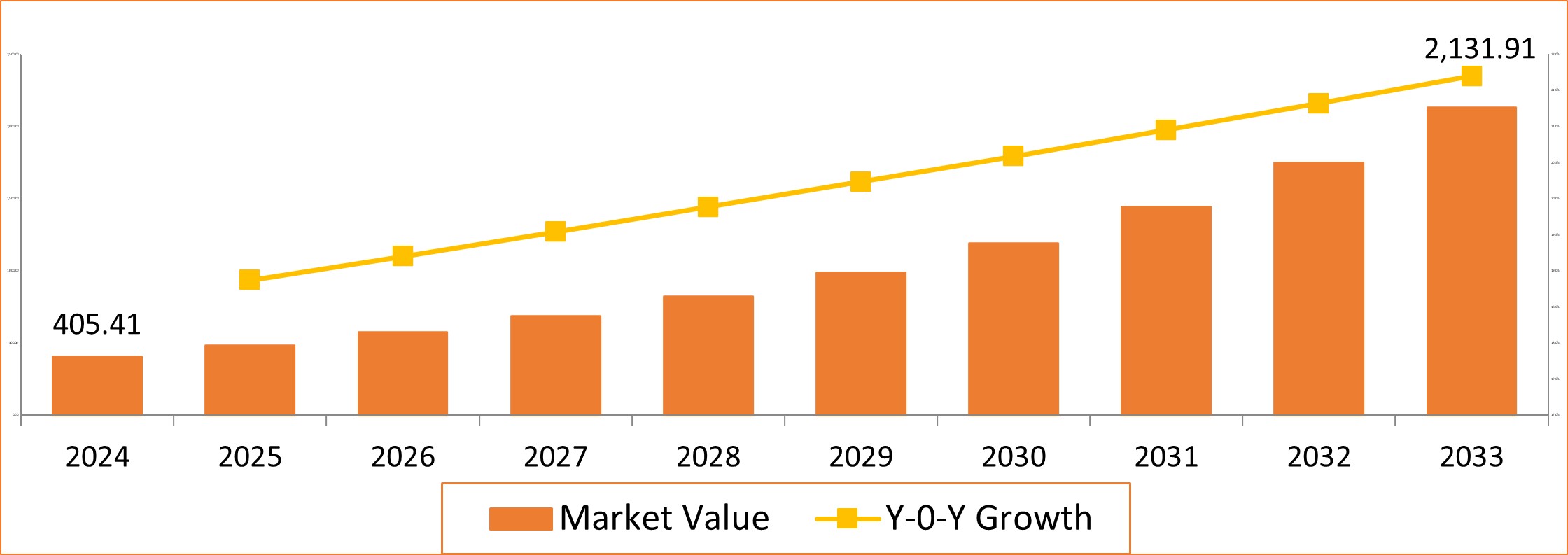
Current Market Landscape
Top Key Players

Blooming Factors for Stem Cell Therapy
The promise of Stem Cell Therapy in Heart Diseases
Stem cell therapy has emerged as a promising approach for treating heart diseases, utilizing the regenerative capabilities of stem cells to repair damaged cardiac tissues. Stem cell therapy has demonstrated significant potential in regenerating damaged cardiac tissue, especially following myocardial infarctions (heart attacks). This therapy aims to restore heart function by promoting the repair and regeneration of heart muscle, providing an alternative to traditional treatments that primarily manage symptoms without addressing the underlying tissue damage.
For instance, in August 2024, an innovative clinical trial is currently underway at the University of Louisville (UofL) and UofL Health, focusing on a new stem cell therapy for heart failure. This trial is notable for several reasons, marking significant advancements in the field of regenerative medicine.
This trial is the first in the United States to test umbilical cord-derived stem cells specifically for heart failure treatment. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs) are harvested from donated umbilical cords, which are rich in stem cells that have the potential to differentiate into various cell types. This source of stem cells is advantageous because it provides a plentiful supply and avoids ethical concerns associated with embryonic stem cells.
Challenges in the Stem Cell Therapy
One of the major challenges in stem cell therapy is effectively delivering stem cells to the heart. The delivery method is crucial for ensuring that the cells reach the target site and integrate into the damaged tissue. Various methods are being explored, including intravenous injection is a non-invasive method that may lead to low retention rates in the heart, intracoronary injection directly delivers stem cells into the coronary arteries, allowing for targeted delivery and direct myocardial injection: involves injecting stem cells directly into the heart muscle, which can enhance local concentration but carries risks of injury and cell washout.
Also, high treatment costs are a significant constraint in the stem cell therapy market, affecting patient access and overall market growth. According to the DVC, stem data stated that the costs associated with stem cell therapies can vary widely, ranging from $5,000 to USD 50,000, depending on various factors. This variability can deter patients and healthcare providers from pursuing these innovative treatments, despite their potential benefits.
Opportunities in the Stem Cell Therapy
Advancements in regenerative medicine are significant opportunities for growth in the global stem cell therapy market, the ongoing evolution, and integration of innovative techniques and technologies aimed at enhancing patient outcomes. This field focuses on repairing, replacing, or regenerating damaged tissues and organs, frequently utilizing stem cells due to their unique regenerative properties. For instance, in September 2024, Poseida Therapeutics, Inc. announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT) designation to P-BCMA-ALLO1, an investigational allogeneic CAR-T cell therapy based on stem cell memory T cells (TSCM).
Pipeline Analysis of Stem Cell Therapy
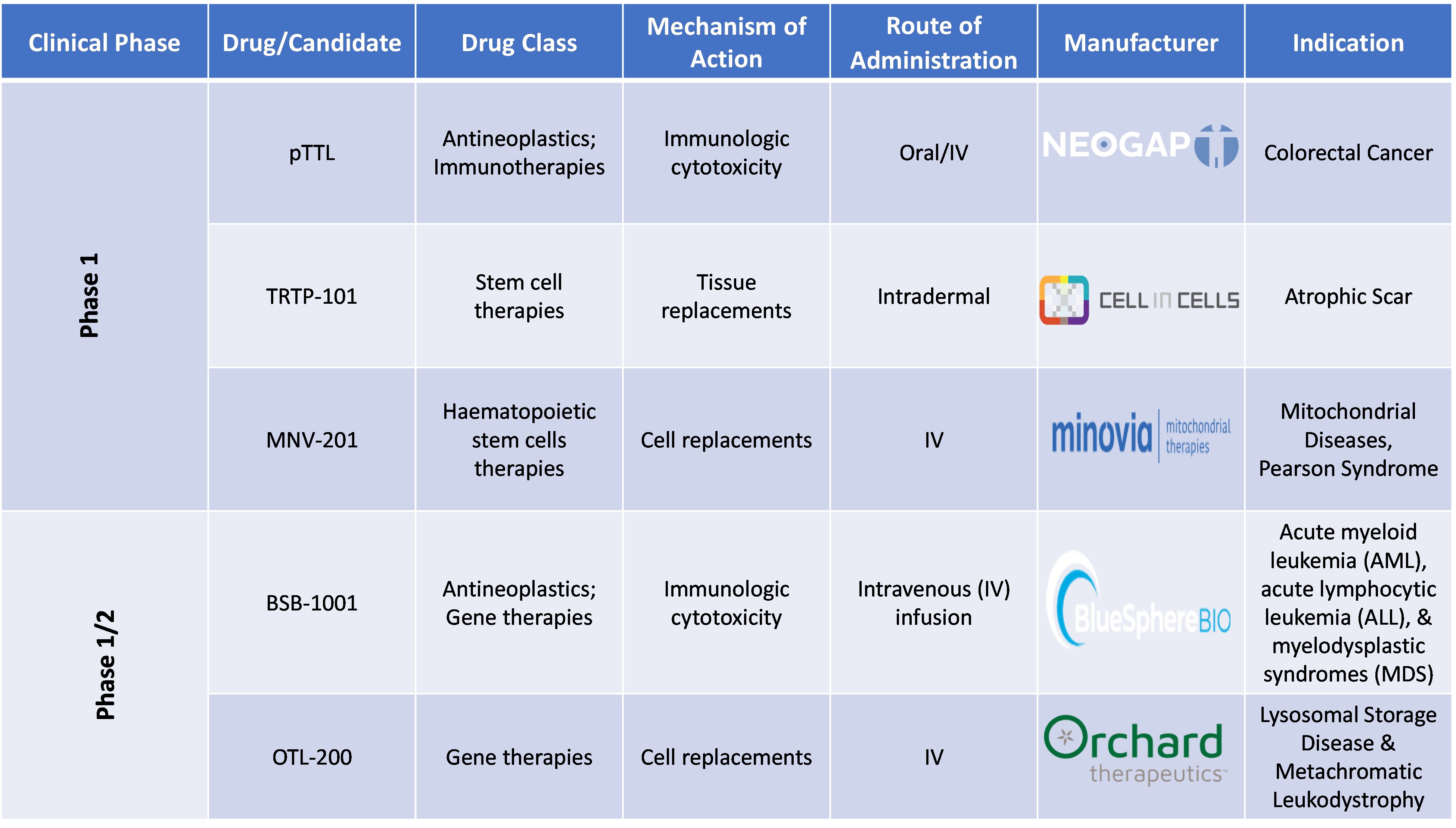
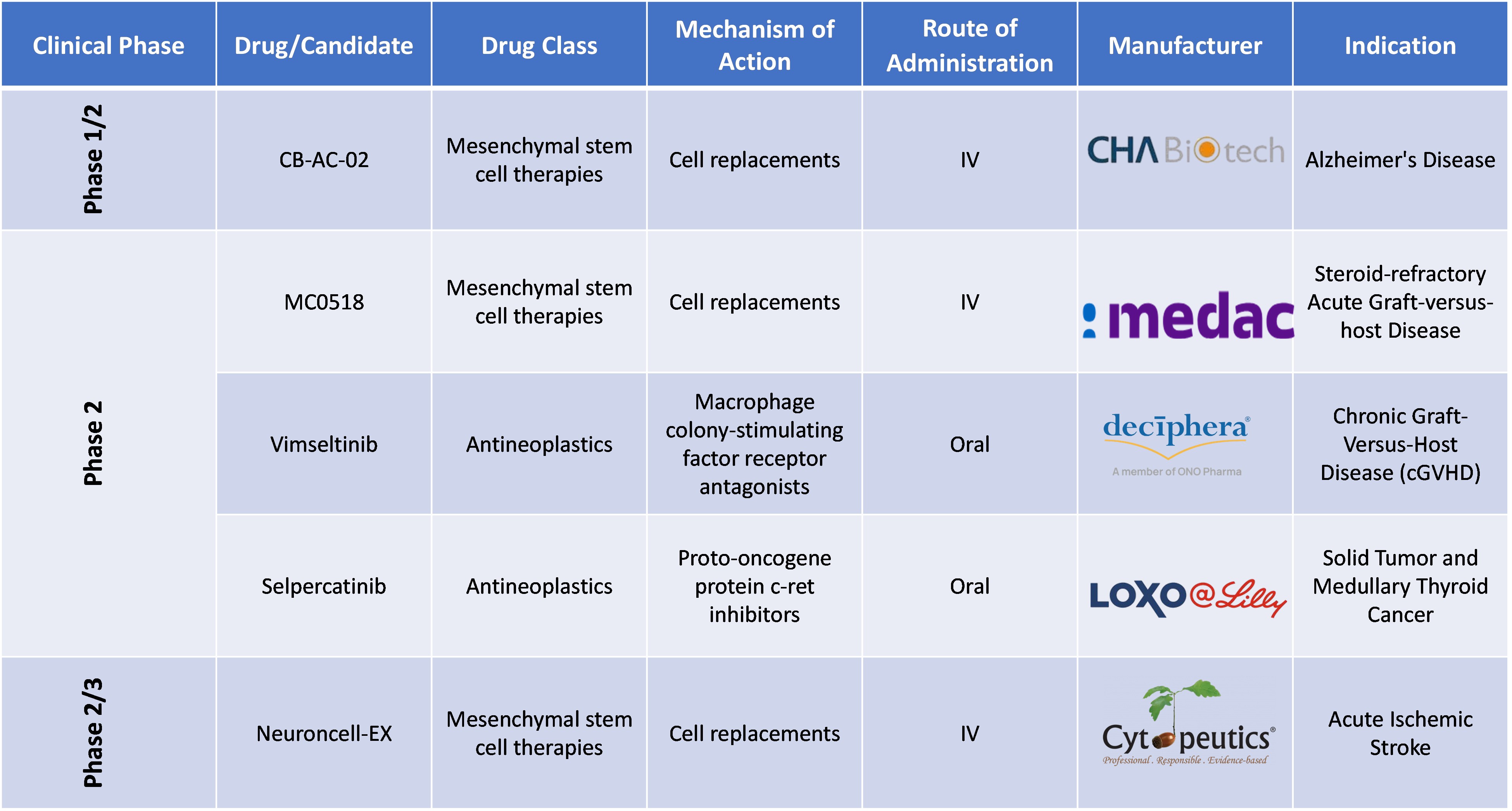
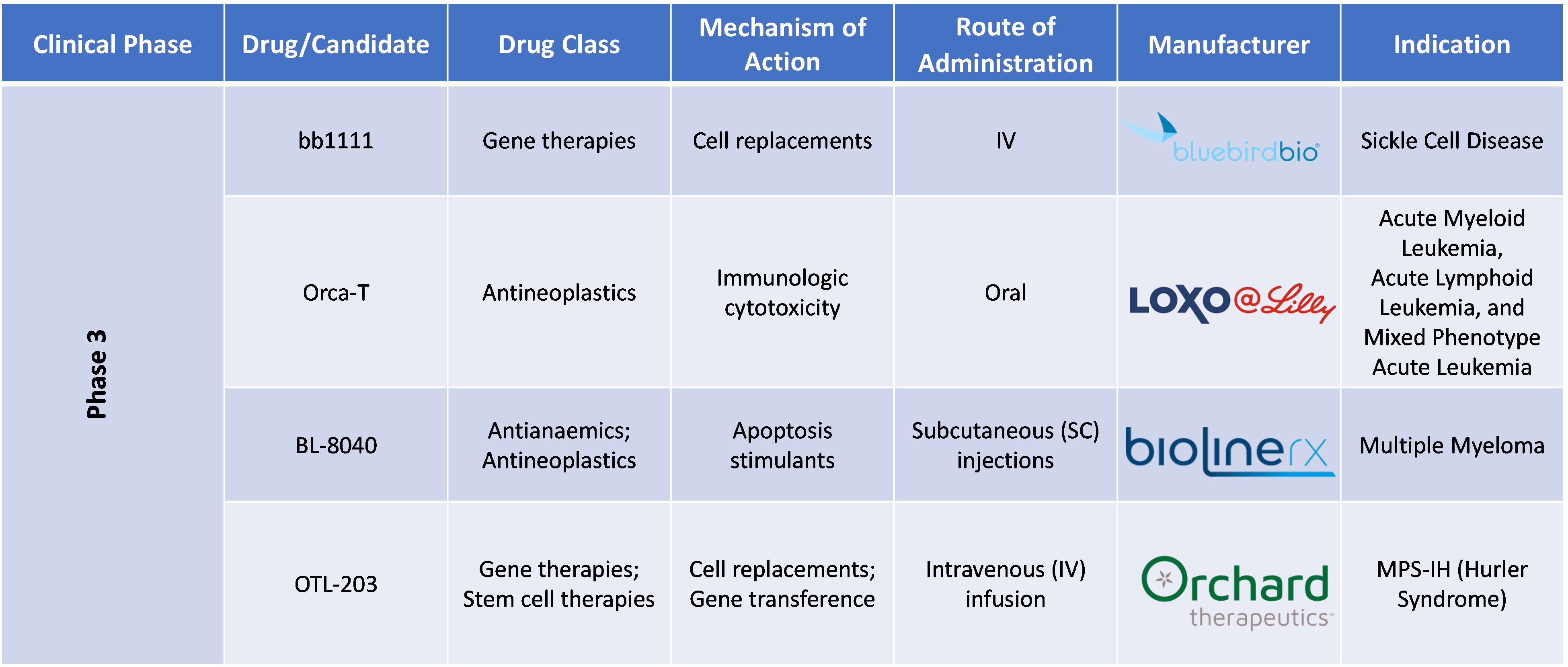
Conclusion
The future of stem cell therapy is on the brink of transformative advancements that could redefine treatment paradigms across various medical fields. Stem cell therapy is at the forefront of modern medicine, presenting unprecedented opportunities to treat previously untreatable conditions through its unique regenerative capabilities. Stem cell therapy is bright, characterized by a convergence of scientific innovation and clinical application that holds the potential to revolutionize healthcare. As research progresses and new therapies emerge, stem cell therapy may not only improve individual patient outcomes but also transform our understanding of disease treatment and prevention in the years to come.

