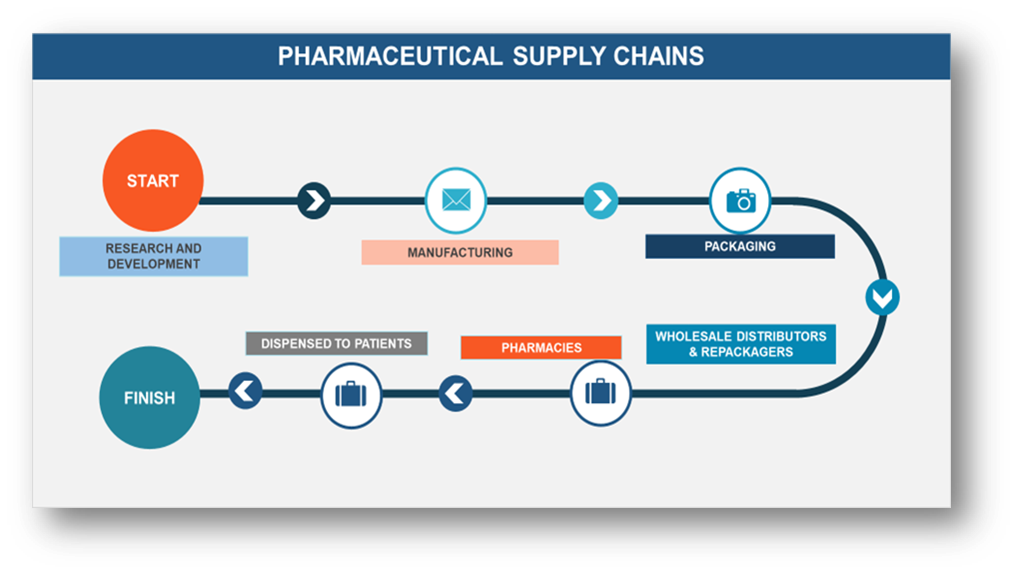
Cold chain logistics plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safe and effective distribution of temperature-sensitive pharmaceutical products, such as vaccines, biologics, and specific medications. These products require strict temperature controls to preserve their efficacy, safety, and quality as they travel from manufacturers to end users. With the continued expansion of the pharmaceutical industry, the importance of efficient cold chain management has grown significantly, especially during global health crises like the COVID-19 pandemic.
In the past decade, pharmaceutical cold chain logistics has experienced rapid innovation and growth. The increasing demand for biologics and other temperature-sensitive medicines has heightened the need for reliable, temperature-controlled distribution systems. In the early 2000s, a specialized focus on cold chain logistics emerged, driven by a collaborative effort among industry experts to promote awareness and standardize best practices. As a result, new technologies and methods were developed to protect shipments and maintain precise temperature conditions throughout the supply chain. Regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA have played a crucial role in ensuring that pharmaceutical products are transported safely, maintaining the integrity of cold chain logistics to ensure product efficacy and safety.
With advancements in cold chain storage, temperature monitoring, and distribution systems, the pharmaceutical industry can now meet the growing demand for biologics, vaccines, and other cold chain products, ensuring that these critical medications are delivered under optimal conditions, no matter where in the world they are needed.
The pharmaceutical cold chain logistics industry is a vital and rapidly growing sector, crucial for the safe transportation and storage of temperature-sensitive products such as vaccines, biologics, and other life-saving medications. Valued at $17.9 billion in 2023, according to DataM Intelligence, the industry is expected to keep expanding, driven by various key factors.
COVID-19: A Catalyst for Change in Cold Chain Logistics
The pandemic acted as a wake-up call, expanding the perspective on cold chain logistics beyond traditional risk assessments, which typically focused on validating packaging and trade lanes. The global response to the pandemic also led to a wave of technological advancements. The rapid deployment of new equipment and infrastructure, including refrigerated ocean containers and data loggers connected to cellular networks, set the stage for more efficient and reliable cold chain logistics. Companies such as CSafe, Cryoport, Sonoco ThermoSafe, and Envirotainer have been at the forefront of developing innovative solutions to meet the growing demand for temperature-controlled shipping.
Regulatory Standards and Guidelines for Cold Chain Management in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Cold chain management is crucial for maintaining the safety and efficacy of temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals like vaccines and biologics. Regulatory compliance is essential, with standards set by bodies such as the FDA, EMA, WHO, USP, and ASTM.
FDA Regulations: In the United States, the FDA provides comprehensive guidelines for cold chain management, primarily through the Good Distribution Practices (GDP) and current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP). These regulations ensure that pharmaceutical products are stored, handled, and transported under appropriate conditions to maintain their safety, efficacy, and quality.
- 21 CFR Part 211: Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Part 211 – Current Good Manufacturing Practice for Finished Pharmaceuticals
- 21 CFR 205.50: Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Part 205 – Good Distribution Practice for Prescription Drugs
- 21 CFR 203.32: Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Part 203 – Regulations for Drug Samples
- FDA Guidance for Industry: Process Validation: U.S. Food and Drug Administration Guidance for Industry – Process Validation
EMA Regulations: The European Medicines Agency (EMA) sets out strict cold chain requirements for pharmaceutical distribution within the European Union.
- EU Guidelines for GDP of Medicinal Products: European Union Guidelines for Good Distribution Practice of Medicinal Products
- European Commission’s Guideline 2015/C 95/01: European Commission’s Guideline on Good Distribution Practice (GDP) of Medicinal Products for Human Use
- Regulation (EC) No 178/2002: European Commission Regulation (EC) No. 178/2002 – General Food Law Regulation, also applicable to temperature-sensitive medicinal products
- EU Annex 11: European Union Annex 11 – Computerized Systems for cold chain monitoring
WHO Guidelines: The World Health Organization (WHO) offers internationally recognized standards for the storage and transportation of vaccines and other time- and temperature-sensitive pharmaceutical products.
- WHO Technical Report Series, No. 961, Annex 9: World Health Organization (WHO) Technical Report Series, No. 961, Annex 9 – Guidelines on the Storage and Transport of Vaccines
- WHO Guidelines on the International Packaging and Shipping of Vaccines: World Health Organization (WHO) Guidelines on the International Packaging and Shipping of Vaccines
USP Standards: The USP plays a pivotal role in setting standards for the storage, handling, and transportation of pharmaceuticals, providing guidelines that align with regulatory expectations in the U.S.
- USP General Chapter <1079>: United States Pharmacopeia (USP) General Chapter 1079 – Good Storage and Distribution Practices for Drug Products
- USP General Chapter <659>: United States Pharmacopeia (USP) General Chapter 659 – Packaging and Storage Requirements for Pharmaceuticals
- USP General Chapter <1118>: United States Pharmacopeia (USP) General Chapter 1118 – Monitoring Devices for Time, Temperature, and Humidity in Cold Chain Management
Other Key Standards: Several additional organizations and standards contribute to cold chain best practices within the pharmaceutical industry
- ASTM International: ASTM International – Formerly known as the American Society for Testing and Materials, it sets standards for performance and packaging testing of cold chain shipping containers.
- ISPE: International Society for Pharmaceutical Engineering – Provides best practices and guidance for the pharmaceutical industry, including cold chain management.
Advances in Cold Chain Technology
New technologies continue to fill gaps in existing cold chain practices, with a focus on improving temperature reliability, reducing costs, and enhancing packaging solutions. CSafe, for instance, introduced a pallet-size air freight container capable of maintaining -20°C, complementing its 2-8°C containers. Sonoco ThermoSafe developed the Pegasus unit-load device (ULD), which, certified by air carriers, provides up to 300 hours of temperature control at 2-8°C. The use of passive units like the Pegasus ULD and active units like Cryoport's Elite container (designed for ultracold shipments at -80°C) demonstrates the growing sophistication of cold chain technologies.
Additionally, the increasing importance of low-temperature shipping is evident with the advancement of ultracold storage solutions for cell and gene therapies (CGTs). Companies like Cryoport have led the way in providing shipping solutions that maintain cryogenic temperatures, essential for handling highly sensitive biologics, including the innovative mRNA-based vaccines used during the pandemic.
The pharmaceutical industry is undergoing a technological revolution in its cold chain logistics operations. With the growing demand for temperature-sensitive treatments, including biologics, vaccines, and gene therapies, the need for more advanced cold chain solutions has never been greater. Leading the charge in cold chain innovation are technologies such as virtual “control towers,” AI-driven predictive analytics, and advanced smart packaging systems, which are set to redefine how temperature-sensitive shipments are managed, tracked, and delivered.
Virtual Control Towers and Real-Time Tracking
At the forefront of these advancements are virtual "control towers," which leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and predictive analytics to create digital twins of pharmaceuticals and their components throughout the supply chain. These digital replicas allow logistics managers to monitor the location and condition of shipments in real-time, providing crucial information such as whether a package has been opened or if its internal temperature has fluctuated outside the required range. This enhanced visibility allows for more informed decision-making and proactive management of potential disruptions.
In addition, these control towers are powered by the Internet of Things (IoT) monitoring devices, such as RFID, cellular, and satellite-enabled tags, which capture and transmit essential data from shipments in transit. With this technology, pharmaceutical companies can gain insight into every stage of the supply chain, ensuring the integrity of temperature-sensitive products, especially when facing global challenges like the COVID-19 pandemic.
Sustainability and Reducing Emissions
As regulations surrounding greenhouse gas emissions become stricter, pharmaceutical companies must address not only the transportation emissions associated with cold chain logistics but also those linked to refrigeration equipment. For instance, Merck has increasingly turned to ocean freight, which is more environmentally friendly than air transport.
Advancing Cold Chain Technologies
Companies like Lineage, Americold, and United States Cold Storage are advancing cold chain technologies for ultra-low temperatures needed for biologics and gene therapies. They utilize warehouse robotics, smart software for transport optimization, and sensors to ensure goods stay cold. EMBALL'ISO has developed phase change materials for packaging that absorb heat, maintaining cold temperatures. AI-powered technologies are also transforming logistics. For example, TransVoyant's supply chain tracking system and CargoSense's AI-driven predictions helped ensure life-saving vaccines were delivered under proper conditions, especially during the pandemic, preventing disruptions in the cold chain.
Smart Packaging and Tracking Innovations
AeroSafe Global has pioneered smart packaging systems that maintain internal temperatures without refrigeration, demonstrated by successfully keeping ice cream bars frozen during a four-day trip. Additionally, their partner Tag-N-Trac offers Bluetooth and cellular trackers for real-time shipment visibility, improving the tracking and monitoring of temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals. This intelligent labeling technology enhances transparency, reduces the risk of temperature excursions, and enables proactive management of cold chain logistics.
The Growth and Future of Pharmaceutical Cold Chain Logistics
The pharmaceutical cold chain market has experienced rapid growth over the past decade, often outpacing the pharmaceutical industry itself. Cold chain shipments have consistently grown at a rate double that of the industry overall. However, recent years have seen a slight plateau, driven in part by a decline in new FDA drug approvals. Despite this, emerging therapies, biosimilars, and the ongoing demand for biologics continue to fuel the growth of the pharmaceutical cold chain.
In particular, the introduction of biosimilars, such as those targeting Humira (adalimumab), a blockbuster biologic, has opened up new opportunities for the cold chain logistics market. As more biologics face competition from biosimilars, the logistics industry is poised to meet the growing demand for temperature-controlled shipping, ensuring that these products are delivered safely and efficiently.
Another key trend influencing the future of the pharmaceutical cold chain is the increasing reliance on home delivery services for healthcare and pharmaceuticals. Companies like UPS Healthcare are expanding their offerings in home delivery, a trend accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic. With the continued growth of e-commerce and home-based healthcare, the demand for cold chain logistics in home delivery will continue to rise, presenting new challenges and opportunities for logistics providers.
Challenges in Cold Chain Logistics
Cold chain logistics for pharmaceuticals is complex, involving temperature-controlled transportation across various stages of the supply chain. Pharmaceuticals travel long distances, using multiple transport modes like trucks, planes, and ships, each requiring specific temperature controls. Inconsistent temperature monitoring, especially in regions with underdeveloped infrastructure or during emergencies, can lead to temperature excursions, compromising product safety. Robust monitoring systems, including real-time tracking devices and GPS-enabled sensors, are essential to prevent issues like power failures or equipment malfunctions. Companies like FedEx provide advanced temperature-controlled solutions. Additionally, biopharmaceuticals, including cell and gene therapies, require even stricter controls, leading to the development of specialized storage and transport solutions, such as phase change materials and refrigerated containers, offered by companies like Kuehne + Nagel and Lineage Logistics.
The Growth and Future of Pharmaceutical Cold Chain Logistics
The pharmaceutical cold chain market has experienced rapid growth over the past decade, often outpacing the pharmaceutical industry itself. Cold chain shipments have consistently grown at a rate double that of the industry overall. However, recent years have seen a slight plateau, driven in part by a decline in new FDA drug approvals. Despite this, emerging therapies, biosimilars, and the ongoing demand for biologics continue to fuel the growth of the pharmaceutical cold chain.
In particular, the introduction of biosimilars, such as those targeting Humira (adalimumab), a blockbuster biologic, has opened up new opportunities for the cold chain logistics market. As more biologics face competition from biosimilars, the logistics industry is poised to meet the growing demand for temperature-controlled shipping, ensuring that these products are delivered safely and efficiently.
Another key trend influencing the future of the pharmaceutical cold chain is the increasing reliance on home delivery services for healthcare and pharmaceuticals. Companies like UPS Healthcare are expanding their offerings in home delivery, a trend accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic. With the continued growth of e-commerce and home-based healthcare, the demand for cold chain logistics in home delivery will continue to rise, presenting new challenges and opportunities for logistics providers.

